Home-Related Tax Deductions
Tax season. Just the words can send shivers down your spine. But if you’re a homeowner, there’s a silver lining: potential savings!
You’ve probably heard that you can deduct the interest you pay on your mortgage — but did you know there are many other ways homeowners can reduce their tax burden?
Before you start your return, read this post for common home-related tax deductions, eligibility requirements, and tips on how to maximize your savings.
Home-Related Tax Savings: The Basics
Before we get into the details, it’s important to define some important terms to set the stage.
Tax Deductions vs. Tax Credits
Most tax savings opportunities for homeowners come in the form of tax deductions. Deductions work by reducing your taxable income — essentially, the government allows you to subtract certain expenses from your total income before calculating how much you owe in taxes. This means a lower taxable income and, ultimately, a lower tax bill. For example, if you earn $50,000 and claim tax deductions worth $5,000, you will only pay taxes on $45,000.
Tax credits, on the other hand, directly reduce your tax bill, rather than your taxable income. That means that if you owe $10,000 in taxes and claim a tax credit worth $2,000, your tax bill will be reduced to $8,000.
Pro Tip: Meticulous record-keeping is crucial. Keep detailed records of all potentially eligible expenses. This will make tax time much smoother and ensure you don’t miss out on any deductions.
Itemized Deductions vs. Standard Deduction
To understand what deductions apply to your situation, it’s important to know the difference between itemized deductions and the standard deduction. The standard deduction is a fixed dollar amount that you can subtract from your adjusted gross income (AGI) regardless of your actual expenses. Itemized deductions, on the other hand, are specific expenses that you can deduct, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable contributions.
You’ll need to choose whether to itemize or take the standard deduction. Generally, you should itemize if your total itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction. Most home-related deductions are only applicable if you choose to itemize.
2025 Standard Deduction Amounts
- Single and Married Filing Separately: $15,000
- Head of Household: $22,500
- Married Filing Jointly: $30,0001
Source: IRS
Key Home-Related Tax Deductions and Credits
If you do choose to itemize your taxes, common tax deductions and credits available to homeowners include:
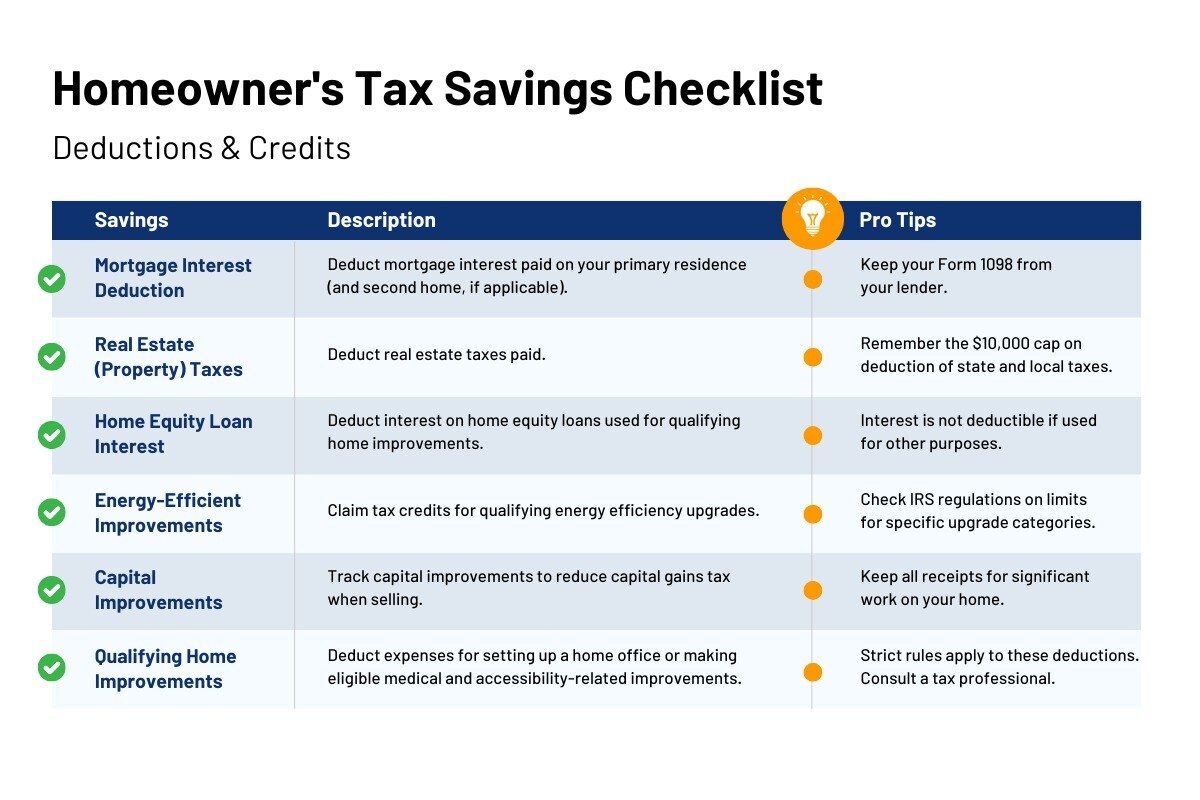
Mortgage Interest Deduction
No one likes to pay mortgage interest, but the good news is that you can deduct interest used to buy or build your primary residence or a second home. However, there are certain limitations that you need to be aware of.2
Mortgage size: If you file your taxes single or married filing jointly, you can deduct interest paid on the first $750,000 of mortgage debt3 for your primary residence or second home. If you are married but choose to file separately, that limit drops to the first $375,000 (for each partner).
Requirements:
- The mortgage interest deduction only applies if your home is collateral for the loan (which is standard).
- To qualify as a primary home, your property must have sleeping, cooking, and toilet facilities.
- If you are deducting mortgage interest on a second home, you don’t need to use the home during the year; however, if you rent it out, you must spend at least 14 days or more than 10% of the days you rented it out (whichever is longer).
So, how do you calculate how much mortgage interest you’ve paid?
The amount of interest you pay each year will vary, even if your interest rate is fixed — that’s because mortgage amortization3 means that you pay more interest earlier in the mortgage’s term, and more principal closer to the end. Each year, your lender will send you (and the IRS) a copy of Form 1098, which shows how much you paid in interest.4
For example, let’s say you are a married homeowner filing jointly with a mortgage for $400,000. If your Form 1098 shows that you paid $25,000 in mortgage interest in 2025, you could deduct the full $25,000 from your 2025 household income.
Real Estate Taxes (Property Taxes)
You can deduct state and local real estate taxes (property taxes) you pay on your primary residence or second home. However, it’s crucial to understand what qualifies. Only property taxes imposed for “general public welfare” are deductible5—if your town imposes a special assessment for a project that directly improves your property value, like a sewer line, that is not deductible. Furthermore, fees for local services, such as trash collection or sewer maintenance, are not deductible, even though your town may list them on the same bill as your property taxes.
There’s also a limit: the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act imposed a $10,000 cap on the total amount of state and local taxes (SALT)6 you can deduct. This includes state and local income tax (or sales tax) as well as property taxes.
Finally, be aware that the amount you deduct must match the amount actually paid to the tax authority.7 This might differ from what you put into escrow if you pay property taxes through your mortgage lender. Typically, the amount your lender paid to your tax authority is listed on Form 1098.
Home Equity Loan Interest
You can deduct the interest paid on home equity loans or home equity lines of credit, but with a significant caveat. Since 2017, that interest is only deductible if the loan proceeds are used to buy, build, or substantially improve3 your primary residence or second home, and the loan is secured by the home.
If you use the home equity loan for other purposes, such as a vacation, debt consolidation, or purchasing a car, the interest is generally not deductible. If you use part of the loan or line of credit for eligible purchases, and part for non-eligible purchases, only interest incurred on the portion used for eligible spending is deductible.
Loan interest is also not deductible if the funds are used for home improvement projects or repairs that do not “substantially improve” your home. Smaller projects, like repainting or new cabinets, likely do not qualify. However, projects like building an addition, a full kitchen remodel, or installing a new roof should qualify as substantial improvements.
It’s also important to note that home equity loan and HELOC interest rate deductions are subject to the same upper limits3 as mortgages (and are added together with your mortgage for calculation purposes). For example, if you have a $500,000 mortgage and a $300,000 home equity line of credit—which together exceed the $750,000 limit for a married couple—you would only be able to deduct interest paid on the first $750,000 of those combined loans.
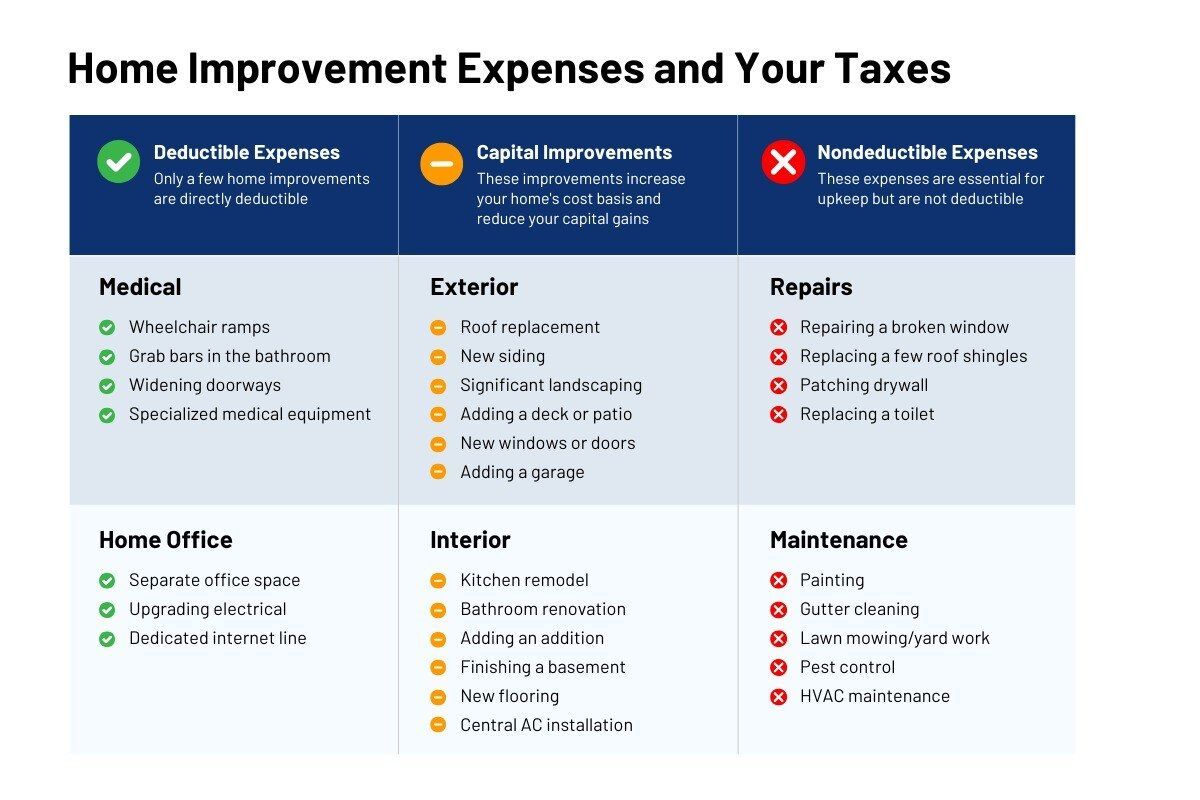
Home Improvement Expenses
You can’t usually deduct home improvement expenses directly.9 However, the money you spend on capital improvements (improvements that increase your home’s value) can help reduce your tax bill later. These expenses are added to your home’s “cost basis,”10 which reduces your capital gains tax when you eventually sell the house. Think of it this way: by keeping records of your home improvements, you’re essentially increasing the “price” you’re considered to have paid for your home, thus lowering your profit when you sell.
It’s important to note that not all projects qualify as capital improvement. Basic repairs and updates likely won’t qualify, while major additions and landscaping likely will (the considerations are the same as those used to determine whether home equity loan interest is deductible).
Beyond capital improvement, there are a few specific categories of home improvement that are deductible, including work on home offices (which is subject to specific limitations) and certain modifications for medical/accessibility reasons.11
Energy-Efficient and Clean Energy Tax Credits
Certain energy-efficient home improvements can qualify you for valuable tax credits. Unlike deductions, which reduce your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce your tax bill, making them even more beneficial.
For qualifying energy efficiency expenses in the 2024 tax year12, homeowners can claim up to 30% of qualified expenses on their federal tax return, with a maximum credit of $3,200.13 However, some qualifying expenses, like new exterior doors and windows, come with their own maximum credit limits, so it’s essential to check the specific rules.
Another option is the Residential Clean Energy Tax Credit, which offers a 30% credit for the cost of installing renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, on your primary residence or a second home that you use part-time and don’t rent out.13 Many states also offer their own tax deductions, rebates, or credits related to energy efficiency and clean energy, so be sure to investigate what’s available in your state.
Selling Your Home and Taxes
When you sell your home, the difference between the selling price and what you originally paid for it (plus any major improvements) is called your capital gain. Think of it as your profit from the sale. Let’s walk through a simple example:
Imagine you bought your home for $200,000. Over the years, you invested in some significant upgrades, like a kitchen remodel ($30,000), a new roof ($15,000), and landscaping ($5,000). These are called “capital improvements,” and they increase your home’s “cost basis”—essentially, what the IRS considers you to have invested in the property. In this case, your adjusted cost basis would be $250,000 ($200,000 original price + $50,000 improvements).
Now, let’s say you sell your home for $350,000. Your capital gain would be $100,000 ($350,000 selling price – $250,000 adjusted cost basis).
Capital Gains Exclusion
The good news is that the IRS allows you to exclude a significant portion of your capital gain from taxation!14 If you’re single, you can exclude up to $250,000, and if you’re married filing jointly, you can exclude up to $500,000. To qualify for this exclusion, you need to have owned and used the home as your primary residence for at least two out of the five years before the sale. This is a key factor to consider when deciding how long you plan to live in a home.
Essentially, this exclusion means that, in many cases, homeowners won’t owe any capital gains tax when they sell their primary residence. It’s a valuable tax benefit that can significantly impact your finances. Keep good records of your purchase price and any capital improvements you make to ensure you can accurately calculate your capital gain and take full advantage of the exclusion when you sell.
Record-Keeping Tips for Homeowners
Organized records are essential for taking advantage of tax deductions and credits. Keep all relevant documents, such as mortgage statements, property tax bills, and receipts for home improvements, readily accessible.15 It’s wise to keep both physical and digital copies (scan and save everything!). Store physical copies securely, perhaps in a safe deposit box. Keep all home-related records for as long as you own the home, plus at least three years after you file your tax returns for the year of the sale.
Conclusion
Homeownership offers numerous opportunities to save on taxes. From mortgage interest and property taxes to energy-efficient upgrades and capital gains exclusions, understanding these deductions and credits can significantly reduce your tax burden. Remember, this information is for general guidance only. Consulting with a qualified tax professional is invaluable for personalized advice.
Have questions about real estate or need a referral to a trusted tax advisor? Contact us today!
Note: This information is intended for general guidance only. Tax regulations are subject to change.
Sources:
- IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/irs-releases-tax-inflation-adjustments-for-tax-year-2025 - Nerdwallet –
https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/taxes/mortgage-interest-rate-deduction - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-publication-936 - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-form-1098 - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/faqs/itemized-deductions-standard-deduction/real-estate-taxes-mortgage-interest-points-other-property-expenses/real-estate-taxes-mortgage-interest-points-other-property-expenses-5#:~:text=The%20total%20deduction%20allowed%20for,taxes%20or%20sales%20taxes)%20is - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc503#:~:text=Overall%20limit,your%20other%20itemized%20deductions%20also. - TurboTax –
https://turbotax.intuit.com/tax-tips/home-ownership/claiming-property-taxes-on-your-tax-return/L6cSL1QoB - Bankrate –
https://www.bankrate.com/home-equity/home-equity-loan-tax-changes/#how-to-claim - USNews –
https://realestate.usnews.com/real-estate/articles/are-home-improvements-tax-deductible - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/publications/p523 - NOLO –
https://www.nolo.com/legal-encyclopedia/what-home-improvements-tax-deductible.html - USNews –
https://money.usnews.com/money/personal-finance/articles/how-consumers-can-save-with-the-new-climate-tax-breaks - IRS –
https://www.irs.gov/credits-deductions/energy-efficient-home-improvement-credit - Bankrate –
https://www.bankrate.com/real-estate/capital-gains-tax-on-real-estate/#avoiding-during-home-sale - NOLO –
https://www.nolo.com/legal-encyclopedia/tax-reasons-keep-good-records-home-improvements.html